Understanding Family Systems Theory: Dynamics, Roles, and Impact
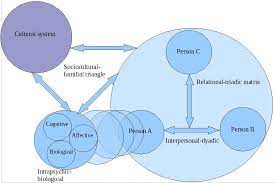
As the cornerstone of society, the family profoundly influences individual development and well-being. The Family Systems Theory, pioneered by psychiatrist Murray Bowen in the 1950s, offers a comprehensive framework for understanding the intricate interplay of relationships within families. This theory posits that families function as interconnected systems, where the behavior of one member inevitably affects the entire unit. This essay aims to probe into the core tenets of Family Systems Theory, exploring its key concepts, the dynamics it encompasses, and its implications for individual and familial dynamics.
Core Concepts of Family Systems Theory
Differentiation of Self
One of the central concepts in Family Systems Theory is the differentiation of self, which refers to an individual’s ability to maintain a sense of self while remaining emotionally connected to the family. Individuals with higher levels of differentiation can navigate relationships with a healthy balance between autonomy and intimacy. Those with lower differentiation tend to be more enmeshed with family dynamics, potentially leading to emotional reactivity and dependency.
Triangles
Triangles represent the basic building blocks of family dynamics. They occur when tension between two individuals leads to the involvement of a third party, acting as a stabilizing force. Triangles can be functional, allowing for the diffusion of anxiety, or dysfunctional, perpetuating conflict and avoidance. Understanding the role of triangles is crucial in assessing family communication patterns and resolving disputes.
Emotional Fusion
Emotional fusion refers to the blurring of emotional boundaries between family members. When emotional boundaries are weak, family members may become overly involved in each other’s lives, leading to enmeshment and heightened emotional reactivity. Developing healthier boundaries is essential for fostering individual autonomy and healthier family dynamics.
Family Roles and Dynamics
Family Roles
Family Systems Theory emphasizes specific family roles, each serving a unique function. These roles, such as the mediator, caretaker, rebel, and scapegoat, help maintain equilibrium within the family system. Nevertheless, parts can contribute to dysfunctional patterns and hinder individual growth when they become rigid or unbalanced.
Communication Patterns
Communication lies at the heart of family systems. Open, honest, and effective communication fosters understanding, empathy, and healthy conflict resolution. Conversely, poor communication, characterized by criticism, avoidance, or defensiveness, can lead to misunderstandings and escalating conflicts. Recognizing and addressing communication patterns is critical for promoting a more functional family system.
Family Life Cycle
Family Systems Theory acknowledges that families evolve, experiencing distinct stages in their life cycle. These stages, such as expansion, formation, and separation, each present unique challenges and opportunities for growth. Understanding the family life cycle enables individuals and families to navigate transitions more easily and adaptable.
Impact on Individual Development
Emotional Well-being
The family environment significantly influences an individual’s emotional well-being. A supportive, nurturing family can foster a sense of security, self-esteem, and emotional resilience. Conversely, a dysfunctional or high-conflict family can lead to anxiety, depression, and low self-worth. Recognizing the impact of family dynamics on emotional well-being is crucial for individuals seeking personal growth and healing.
Interpersonal Relationships
The quality of family relationships sets the foundation for an individual’s approach to interpersonal connections outside the family unit. Healthy family dynamics can provide models for effective communication, conflict resolution, and intimacy. Conversely, dysfunctional family patterns may lead to challenges forming and maintaining healthy relationships with peers, romantic partners, and colleagues.
Applying Family Systems Theory in Practice
Family Therapy
Family Systems Theory is a cornerstone in family therapy, guiding practitioners in understanding the underlying dynamics. Through interventions that focus on improving differentiation, establishing healthy boundaries, and reshaping communication patterns, family therapy aims to promote greater harmony and well-being within the family unit.
Individual Growth and Self-awareness
Understanding the principles of Family Systems Theory can be transformative for individuals seeking personal growth and healing. It provides a framework for self-reflection, allowing individuals to recognize and address patterns from their family of origin. Individuals can navigate relationships and life transitions with greater resilience and authenticity by cultivating a greater sense of differentiation and self-awareness.
Conclusion
Family Systems Theory offers a profound lens through which to understand the complexities of familial relationships. By recognizing family members’ interconnectedness and dynamics’ impact on individual development, individuals can gain insight into their behavior and patterns. Utilizing the principles of Family Systems Theory in therapy and personal growth endeavors empowers individuals and families to foster healthier, more fulfilling relationships and create a foundation for lasting well-being. As Murray Bowen aptly noted, “The family is a system that regulates its members.” Understanding this system can be the key to unlocking greater harmony, growth, and fulfillment within families and individuals.
References:
Lang, D. (2022). Family Systems Theory. iastate.pressbooks.pub. [online] Available at: https://iastate.pressbooks.pub/individualfamilydevelopment/chapter/the-family-systems-theory/.
Watson, W.H. (2012). Family Systems Theory. [online] www.sciencedirect.com. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/family-systems-theory.





