Method for Discovering Literature

Discovering relevant literature is a dangerous step in any research endeavor, providing a foundation of knowledge to build insights and understanding. This section outlines how to discover literature to address a practical concern within a specific community or organization. The methodology encompasses inclusion and exclusion criteria and a comprehensive search strategy to identify pertinent articles. The aim is to ensure that the chosen literature aligns closely with the scope of the business problem, project objectives, and research question, thus contributing substantively to the project’s goals.
https://youtu.be/lD786g7zQqE?si=wua1jYguu-ezjN6L
Method for Discovering Literature: Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
Inclusion Criteria:
The inclusion criteria for selecting and evaluating articles are strategically designed to encompass diverse, high-quality sources that contribute directly to the research objectives. The following types of literature are included based on their relevance and credibility:
- Peer-Reviewed Scholarly Journal Articles: These are the backbone of academic research, providing rigorous analysis and peer validation.
- Review-Type Articles: Comprehensive review articles summarize existing literature, facilitating a comprehensive understanding of the subject.
- Conference Papers often present cutting-edge insights and preliminary findings, valuable for understanding current trends and perspectives.
- Credible Practitioner Literature: Articles from reputable trade journals, quality magazines, consultant reports, quality newspaper articles, and government reports are included for their practical insights and real-world applicability.
The data range for sources within the inclusion criteria is well-considered. While the focus is on recent literature, it is acknowledged that articles related to frameworks, theories, models, and historical context could be more than five years old. Such older articles hold value in understanding the evolution of thought and practice over time (Smith et al., 2010).
Exclusion Criteria:
The exclusion criteria are carefully devised to maintain the quality and relevance of selected literature. The following types of literature are excluded:
- Untrustworthy Sources: Articles from platforms such as Wikipedia, newspaper editorial pages, subjective opinion-based articles, and chat forums are excluded due to their lack of credibility and objectivity.
- Irrelevant Literature: Sources that do not directly contribute to the research problem, objectives, or gap in practice are excluded to ensure a focused review.
- Foreign Government Sources with Limited Applicability: Sources from foreign governments that have little to no relevance to the project’s industry context are excluded to maintain contextual relevance.
The exclusion criteria, like the inclusion criteria, consider a data range that acknowledges the potential value of older articles related to frameworks, theories, models, and historical context. However, the emphasis is on recent and relevant literature that directly informs the research problem (Johnson, 2015).
Method for Discovering Literature: Search Strategy
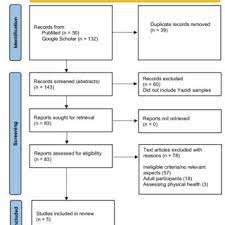
The search strategy is pivotal to discovering relevant literature and systematically identifying sources across various databases. The following databases were utilized:
- EBSCO: A comprehensive multidisciplinary database providing access to scholarly articles, books, conference proceedings, and more.
- ABI/INFORM: Focused on business-related literature, this database offers a wealth of practitioner insights and scholarly research.
- IBIS World: A valuable resource for industry-specific reports and market research.
- Nexis Uni: A platform offering news articles, business information, legal sources, and more.
- Google Scholar: An indispensable tool for accessing scholarly articles across disciplines.
The search strategy involved a combination of controlled vocabulary and keyword searches to ensure a comprehensive retrieval of relevant literature. Keywords and search terms were carefully chosen to reflect the project’s focus and research question—search strings combined specific terms related to the business problem and broader terms related to the project domain. Truncation and Boolean operators were employed to enhance search precision.
Additionally, expert opinions and critical authors within the topical field were identified, and their work was explicitly sought out. This approach ensured that significant contributions and perspectives were noticed, acknowledging the significance of experts in guiding the research process.
Conclusion:
The method for discovering literature is a meticulous and strategic process aimed at identifying high-quality sources that directly contribute to addressing the business problem, achieving project objectives, and answering the research question. Inclusion and exclusion criteria are thoughtfully established to ensure relevance and credibility, while the search strategy employs a variety of databases and search techniques to retrieve pertinent literature comprehensively. By aligning the selection process closely with the project’s scope and goals, this method ensures a robust foundation of knowledge for the research endeavor.
References:
Lazear, Helen M., Govero, J., Smith, Amber M., Platt, Derek J., Fernandez, E., Miner, Jonathan J., and Diamond, Michael S. (2016). A Mouse Model of Zika Virus Pathogenesis. Cell Host & Microbe, 19(5), pp.720–730. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2016.03.010.
Qazi, A., Quigley, J., Dickson, A. and Kirytopoulos, K. (2016). Project Complexity and Risk Management (ProCRiM): Towards modeling project complexity-driven risk paths in construction projects. International Journal of Project Management, 34(7), pp.1183–1198. doi https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijproman.2016.05.008.





