Analysis of the Global Automobile Industry: Opportunities and Threats
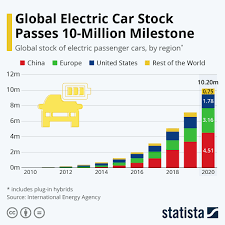
The global automobile industry is pivotal in the modern economy, contributing to technological advancements, mobility solutions and employment generation. This analysis aims to assess the industry’s attractiveness through Porter’s Five Forces analysis, analyse its general environment using the PESTEL framework, and subsequently identify strategic opportunities and threats for major automobile manufacturers.
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis of the Global Automobile Industry
Threat of New Entrants:
The threat of new entrants is relatively moderate in the global automobile industry. High capital requirements, established brand recognition and economies of scale are barriers to entry. Additionally, the need for substantial research and development investments to meet regulatory and technological demands poses challenges for new entrants.
Bargaining Power of Suppliers:
Suppliers in the automobile industry possess moderate bargaining power. Automakers rely on a complex network of suppliers for components, technology and materials. Nevertheless, multiple suppliers and the potential to switch suppliers mitigate their bargaining power.
Bargaining Power of Buyers:
Buyers in the automobile industry, such as consumers and fleet operators, have varying levels of bargaining power. Their preferences, influenced by factors like brand loyalty, innovation, and pricing, dictate their influence on manufacturers. Numerous automobile options provide buyers with choices and reduce their bargaining power.
Threat of Substitutes:
The threat of substitutes in the automobile industry is moderate. Public transportation, ride-sharing services, and alternative modes offer viable alternatives to owning personal vehicles. However, the cultural significance of car ownership and the lack of comparable options in certain regions mitigate the threat.
Intensity of Competitive Rivalry:
Competitive rivalry is high in the automobile industry. Intense competition among global manufacturers drives innovation, product differentiation, and cost efficiency. The industry’s maturity and numerous players’ presence contribute to aggressive market share competition.
Overall Industry Attractiveness:
Considering the five forces, the global automobile industry can be regarded as moderately attractive. While entry barriers and competition are relatively high, technological advancements, established brand value, and consumer demand contribute to the industry’s allure.
PESTEL Analysis of the General Environment
Political Factors:
Political factors such as emission standards, government regulations, and trade policies significantly influence the automobile industry. Evolving fuel efficiency and emissions regulations drive manufacturers to invest in research and development for cleaner technologies.
Economic Factors:
Exchange rates, economic conditions, and consumer spending patterns influence the industry’s health. Economic downturns can lead to decreased consumer purchasing power and affect automobile demand.
Sociocultural Factors:
Sociocultural trends shape consumer demand, including preferences for sustainable products and urbanisation. They are furthermore, changing attitudes toward car ownership and the rise of ride-sharing services impact manufacturers’ strategies.
Technological Factors:
Rapid technological advancements, such as electric vehicles, autonomous driving, and connectivity, disrupt traditional business models. Manufacturers must invest in innovation to stay competitive.
Environmental Factors:
Growing environmental concerns drive the industry toward sustainable practices and cleaner technologies. Regulatory pressure and consumer demand for environmentally friendly options impact business decisions.
Legal Factors:
Legal factors encompass regulations related to safety, intellectual property, emissions, and labour practices. Compliance with these regulations is vital for manufacturers to operate ethically and avoid legal challenges.
Strategic Opportunities and Threats
Opportunities:
Electric Mobility: Transitioning toward electric vehicles presents a significant opportunity for manufacturers to meet regulatory requirements, address environmental concerns, and cater to consumers seeking sustainable options.
Autonomous Driving: Advancements in autonomous technology provide opportunities for manufacturers to improve safety, convenience, and accessibility in their vehicles.
Connected Vehicles: Integrating connectivity features offers opportunities to provide personalised services, improve user experiences, and gather valuable data for business insights.
Threats:
Regulatory Uncertainty: Frequent regulation changes related to emissions and safety standards can interrupt business plans and require costly adjustments.
Competition from New Entrants: Emerging players in electric vehicles and technology disruptors entering the automobile space pose threats to established manufacturers.
Supply Chain Disruptions: Dependence on complex global supply chains exposes manufacturers to risks related to disruptions, geopolitical issues, and availability of critical components.
Conclusion Global Automobile Industry
In conclusion, the global automobile industry presents opportunities and threats for major manufacturers. Porter’s Five Forces analysis suggests that while competition and entry barriers are high, established brands and technological advancements contribute to the industry’s moderate attractiveness. PESTEL analysis highlights the industry’s sensitivity to political, economic, sociocultural, technological, environmental, and legal factors, which impact strategic decision-making. Electric mobility, autonomous driving, and connected vehicles emerge as critical opportunities, while regulatory uncertainty, new entrants, and supply chain disruptions pose threats. Manufacturers must navigate these complexities as the industry evolves to capitalise on opportunities and mitigate threats.
References to the Global Automobile Industry
RSM Global. (2023). 2023 outlook: Rising trends in the automotive industry. [online] Available at: https://www.rsm.global/insights/2023-outlook-rising-trends-automotive-industry.
Wagner, I. (2008). Topic: Automotive Industry. [online] www.statista.com. Available at: https://www.statista.com/topics/1487/automotive-industry/.





