The Sociological Perspective on the Economy: Understanding the Interplay between Society and Economic Systems
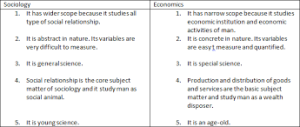
Sociology offers a unique lens through which to analyze and understand the economy. Examining the Sociological Perspective on the Economy gives us insights into the complex interactions between society and economic systems. This essay aims to explore the sociological perspective on the economy, highlighting its usefulness in studying economic phenomena. Drawing on sociological theories and concepts, we will delve into critical areas such as social stratification, power relations, labor markets, globalization, and the impacts of economic policies on different social groups. Ultimately, sociology enables us to go beyond traditional financial analysis by considering the broader social context in which economic activities occur.
Sociology Perspective on the Economic Dynamics and Power Relations
Social Stratification and Economic Inequality:
One crucial aspect of the sociological perspective on the economy is its examination of social stratification and economic inequality. Sociologists emphasize how economic systems produce and perpetuate unequal distributions of resources and opportunities among individuals and social groups. By studying the economy from this perspective, we gain insights into the factors influencing wealth and income disparities. Concepts such as social class, race, gender, and education are instrumental in understanding how social structures shape economic outcomes.
Sociologists highlight the role of power relations in the economic realm, revealing how elites and corporations influence economic policies and resource allocation, often at the expense of marginalized groups. Through this lens, sociology provides a critical understanding of the causes and consequences of economic inequality, enabling us to propose strategies for more equitable economic systems.
Power Relations and Economic Decision-Making :
Sociology helps us examine the intricate power dynamics that shape economic decision-making processes. Financial systems are not value-neutral; social, cultural, and political factors influence them. Sociologists study power distribution among various actors, such as governments, corporations, labor unions, and consumer groups. They analyze how these actors negotiate and compete for resources, influence economic policies, and shape economic outcomes.
This perspective reveals how rational calculations do not solely determine financial decisions but are also influenced by social relationships, ideologies, and interests. By recognizing the influence of power in the economy, sociology offers a comprehensive understanding of economic phenomena and their impact on society.
Sociology’s Analysis of Labor Markets, Globalization, and Economic Policies
Labor Markets and Work :
Sociology sheds light on the dynamics of labor markets and the social experience of work. Beyond the traditional economic analysis of labor as a commodity, sociologists explore how work shapes individuals’ lives and identities. They examine how social factors such as social class, gender, race, and education influence access to employment, job security, and career opportunities. Sociological theories like the conflict perspective highlight the exploitation and alienation experienced by workers within capitalist economies.
Furthermore, sociology explores the social construction of work, including norms, values, and cultural meanings associated with different occupations. By studying the social dimensions of work, sociology contributes to understanding the inequalities, precariousness, and social stratification inherent in labor markets.
Globalization and Economic Change:
Sociology provides valuable insights into the processes and consequences of globalization on economic systems and societies. Globalization involves the integration of economies, cultures, and organizations across borders. Sociologists examine how globalization affects economic structures, production processes, and patterns of inequality. They explore the role of transnational corporations, global financial institutions, and trade agreements in shaping economic outcomes.
Sociology also analyzes the impact of globalization on labor markets, migration patterns, cultural identities, and social movements. By considering the social consequences of globalization, sociology contributes to a more nuanced understanding of economic changes in the contemporary world.
Economic Policies and Social Welfare: The sociological perspective on the economy allows us to critically evaluate financial policies and their implications for different social groups. Sociologists examine how economic policies influence social welfare, access to resources, and opportunities for social mobility.
They explore how taxation, welfare programs, education, and healthcare policies affect different social classes, racial and ethnic groups, and genders. Sociology reveals the unintended consequences of economic policies and highlights the need for a more inclusive and social approach to economic governance. By providing empirical evidence and theoretical frameworks, sociology contributes to evidence-based policy-making and the promotion of social welfare.
In conclusion, The sociological perspective on the economy offers a multifaceted and comprehensive understanding of economic systems and their interplay with society. Sociology enhances our comprehension of economic phenomena beyond traditional economic theories by analyzing social stratification, power relations, labor markets, globalization, and economic policies. It provides a critical lens through which we can evaluate the consequences of financial systems on social inequality, power dynamics, work experiences, globalization processes, and social welfare.
As our world becomes increasingly interconnected, understanding the complex relationships between society and the economy is essential for addressing the challenges of economic inequality, sustainable development, and social justice. Sociology offers invaluable insights into these dynamics, making it a valuable discipline for studying the economy.
References:
- Granovetter, M. (1985). Economic action and social structure: The problem of embeddedness. American Journal of Sociology, 91(3), 481-510. [Link: https://www.journals.uchicago.edu/doi/abs/10.1086/228311]
- Bourdieu, P. (1986). The forms of capital. In J. G. Richardson (Ed.), Handbook of Theory and Research for the Sociology of Education (pp. 241-258). Greenwood Press. [Link: https://www.jstor.org/stable/1176230]
- Fligstein, N., & McAdam, D. (2012). A theory of fields. Oxford University Press. [Link: https://www.oxfordscholarship.com/view/10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199859948.001.0001/acprof-9780199859948]
Sociological Perspective on the Economy





